Models with ActiveRecord
Agenda
- Quiz
- Using Ruby to talk to databases
- Object-relational Mapping (ORM)
- Introduction Active Record
- Required Gems
- Connecting to the Database
- Creating Models
- CRUD with Models
- Create
- Read
- Update
- Destroy
- Lab/Exercise
QUIZ
- What command in
psqlconnects to a database? - What does SQL stand for? What is it meant to do?
- What does
SERIAL PRIMARY KEYdo when assigned to a column? - If I
INSERTinto a Table, what am I doing? - If I
SELECTin a Table, what am I doing?
Using Ruby to talk to databases
- Wouldn't it be nice if you could just talk to databases using Ruby?
- That'd make life a lot simpler, wouldn't it?
- Understanding SQL is important...
- But what if we could make our lives as developers just a little bit easier?
Object-relational Mapping (ORM)
- ORMs are designed to map databases to Objects
- Imagine having an Object that acts as translator between you and SQL!
- It is the Babel Fish of SQL!
- They really simplify development...
- ...and make our lives easier
Human Intention behind Active Record
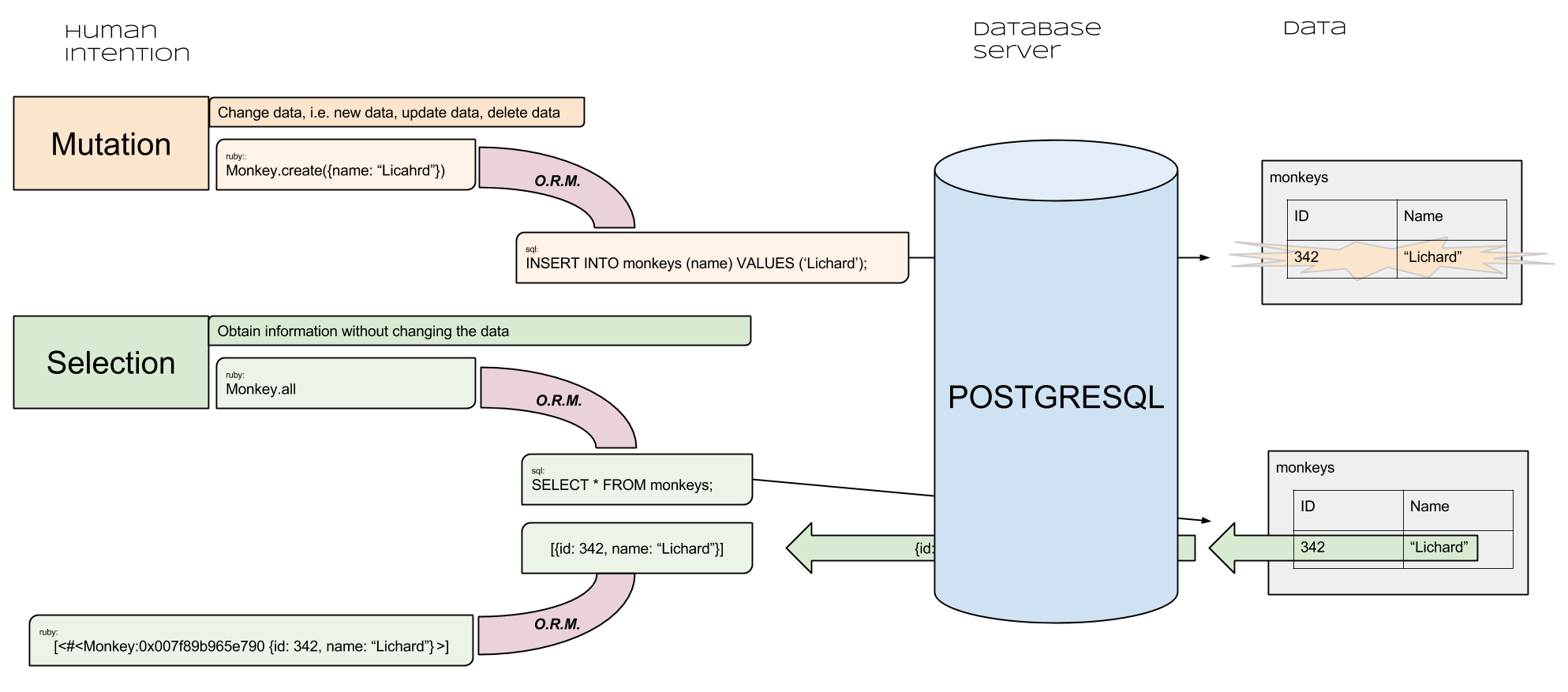
How ORMs Work
- ORMs are designed to perform transactions.
- When a program makes a request to the database, the transaction begins.
- The ORM then translates the request into SQL!
- It then attempts to run the SQL query that it created...!
- It changes are made to the database and the query was successful the changes are committed.
- If the query fails... no changes are made and the transaction is rolled back.
- If this occurs, an error is thrown.
Introduction to ActiveRecord
- ActiveRecord is an ORM written in Ruby
- It was originally designed for Rails
- It has been ported to Sinatra and other languages
- It is realllllllllllllllyyyyyyyy awesome.
Required Gems
You need to include the following libraries in your Gemfile:
gem 'pg' #postgresql
gem "sinatra-activerecord" #activerecord orm
Connecting to the Database
In your application file, you need to establish a connection to your database using ActiveRecord. We do so by calling the establish_connection method that ActiveRecord provides. We'll pass in the following arguments:
:adapter => "postgresql":database => "your_db_name_here"
That's it! From here on out, you can query and modify the database with ease!
Creating Models
- To create a model, we need to create a new file.
- The structure of the naming should be TablenameModel.rb
- We can then include this file using the
require('./TablenameModel')command - A model... is simple.
- Let's take a look at one!
Sample Model
class Students < ActiveRecord::Base
end
Great, isn't it?
CRUD
CRUD stands for 'create', 'read', 'update' and 'destroy'. You perform these actions on tables inside of your database. Let's imagine that you have the following SQL table named Sms:
id | message | sender
-------------------------------------------------
1 | "Hi there!" | "Kathew"
2 | "sup man." | "Lichard"
3 | "Just learned Rails!" | "Kathew"
4 | "hey you guys!" | "Cecelious"
Create
sms = Sms.new # create a new
sms.message = "Hi there!" # add values
sms.sender = "Kathew"
sms.save # saves to the database
Read
Find an object in a list of objects
sms = Sms.find(2) # find by id
# => sms = { id: 2, message: "sup man.", sender: "Lichard" }
sms.message
# => "sup man."
sms[:message]
# => "sup man."
Update
sms = Sms.find(4) # find by id
sms.sender = "sms ninja" # update a value
sms.save # save to database
Destroy
sms = Sms.find(1) # find by id
sms.destroy # delete from database
Conclusion
- Is ActiveRecord awesome?
- Yes?
- Ready to use it?
Lab
Migrations to Models
- We're going to create a students app based on our
dragonsdatabase! - We need to connect to our database!
- We need to create Models for our
Studentstable! - We need to add items using ActiveRecord!
- We need to read them via JSON!